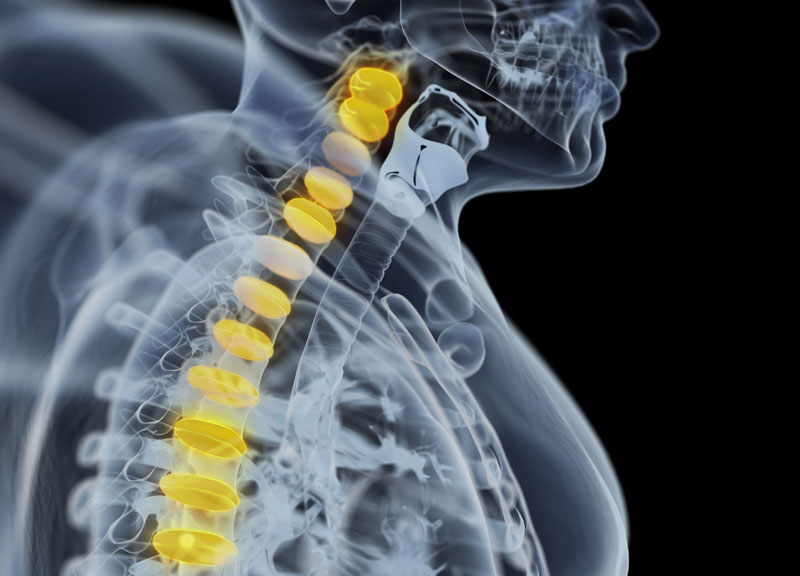
The vertebral column tumor is a growth that develops within the spinal canal or spinal bones. It may either be cancerous or noncancerous. Spinal tumors that start within the spinal cord itself are known as spinal cord tumors. Tumors affecting the vertebrae often metastasize (spread) from cancers in other parts of the body. In some cases, tumors may also originate within the bones of the spine, such as chondrosarcoma, Ewing’s sarcoma, Chordoma, and osteosarcoma.
The Vertebral column tumor may affect the nervous system, leading to impairment of neurological function due to pushing on the spinal cord or adjacent nerve roots. Since these tumors grow into the bone, they may result in pain, instability of the spine, or fractures of the vertebrae. Vertebral tumor is known to life-threatening and lead to permanent disability.
The treatment options may include radiation therapy, surgery, chemotherapy or other medications.
Symptoms of Vertebral Column Tumors
The symptoms shown will depend on the type and location vertebral tumor. The common signs and symptoms may include:
- Pain at the tumor site
- Back pain that radiates to other parts of the body
- Loss of sensation
- Paralysis in varying degrees and in different parts of body
- Muscle weakness (arms or legs)
- Difficulty walking (falls)
- Reduced sensitivity to pain
- Less heat and cold sensitivity
- Loss of bowel or bladder function
When to Seek Medical Help?
Back pain is one of the major symptoms. However, since it can be caused by other reasons, you can see your doctor to discuss back pain if:
- It is persistent and progressive
- Not related to any activity
- It gets worse at night
- You have a history of cancer
- You experience nausea, vomiting or dizziness
Emergency help should be called if you observe:
- Progressive weakness of muscle
- Numbness in legs or arms
- Potential changes in bladder / bowel function
- Causes
Vertebral tumors originating from the spine are very rare. Medical experts suspect defective genes as one of the causes. Most vertebral tumors are caused by other cancerous tumors that have spread from different parts of the body. The cancer is more common among those with a past history of cancer.
Diagnosis
MRI Scan – MRI involves use of a powerful magnet and radio waves for producing images of the spine and accurate viewing of spinal cord and nerves.
Computerized Tomography (CT) Scan – The test produces detailed spine images with a narrow beam of radiation. A contrast dye may also be injected to make abnormal changes in the spinal canal or spinal cord easier to see.
Biopsy – This is the only way to determine whether a tumor is noncancerous or cancerous. A small tissue sample (biopsy) is examined under a microscope during the procedure.
Types of Vertebral Column Tumors
Vertebral tumors are categorized by location, in the spine or vertebral column. The tumors are also referred to as extradural tumors as they occur on the outside of the spinal cord itself.
Metastatic Tumors – Most tumors affecting the vertebrae have spread (metastasized) to the spine from other parts of the body (breast, prostate, kidney or lung).
Cancerous Tumors – These start in the spinal bones and are rare. These include osteosarcomas (osteogenic sarcomas), Ewing’s sarcoma, Chordoma, and chondrosarcoma.
Multiple Myeloma – It is a cancerous disease affecting the bone marrow (spongy inner part of the bone) that makes blood cells.
Noncancerous Tumors – These include osteoblastomas, osteoid osteomas, and hemangiomas.
Treatment Options
Monitoring – Some tumors can be discovered prior to showing any symptoms. This happens when a patient is being evaluated for another condition. Smaller non-cancerous tumors that aren’t growing or compressing adjacent tissues do not need surgery. Careful and regular monitoring will suffice.
Surgery – The procedure is often the main choice for tumors. This helps doctors remove tumors (as much as possible) with an acceptable risk of nerve or spinal cord injury. With advanced technology and the latest techniques and instruments, neurosurgeons can easily reach tumors that were once deemed as inaccessible. Microsurgery is performed with high-powered microscopes to help doctors distinguish a tumor from healthy tissue. Very high-frequency sound waves may also be used in some cases to break up tumors and remove the fragments.
Unfortunately, despite advancements in the medical field, it is not possible to remove the tumor completely. Also the surgery may require a follow-up therapy such as chemotherapy, radiation therapy or both.
Radiation therapy. This may be used following an operation to eliminate the remnants of tumors that can’t be completely removed, treat inoperable tumors or treat those tumors where surgery is too risky.
It also may be the first line therapy for metastatic tumors (those that travel to the spine region from other cancers of the body). Radiation therapy may also be used to relieve pain when no additional therapies are necessary.
Medications – These are helpful in easing some of the side effects of radiation including vomiting and nausea.
Stereotactic Radiosurgery (SRS) – The radiation therapy delivers a very high dose of precisely targeted radiation. Computers are used to focus radiation beams on tumors. This helps with providing doctors pinpoint accuracy. Also the radiation can be given from multiple angles. SRS has certain limitations. It is effective only on a specific size and type of the tumors.
Chemotherapy – This is standard treatment for most types of cancer. The process involves the use of medications to destroy cancer cells or prevent them from growing. It can be given alone or in combination with radiation therapy as required. Patients usually experience side effects, including nausea, fatigue, vomiting, increased risk of infection, hair loss etc.
Drugs – In some cases, doctors prescribe corticosteroids to reduce swelling and inflammation inside spinal cord post surgery or radiation therapy. These are helpful in inflammation but should be used only for short periods to avoid serious side effects. Some of the common side effects of these drugs include osteoporosis, muscle weakness, diabetes, high blood pressure, and increased vulnerability to infection.
Recovery – It may take some weeks or even longer for patients to recover from spinal surgery. This depends on the procedure undertaken or complications involved, such as nerve tissue damage or bleeding.
Alternative Medication
There are no alternative medicines proven to cure cancer. However, some alternative or complementary treatments may provide relief from symptoms.
Acupuncture – The treatment involves the practitioner inserting tiny needles into the patient’s skin at precise points. Research has revealed that acupuncture may be helpful in providing relief from vomiting and nausea. The treatment approach may also provide relief from certain types of cancer.
It is important to consult a doctor prior to trying out an alternative treatment.
Departments and Specialties
Premier Brain and Spine is supported by an experienced team of professionals skilled in specialties. The specialists work together to ensure premium quality care and successful recovery.
The following departments will treat this condition:
- Radiology
- Neurology
- Orthopedic Surgery
- Neurosurgery
- Oncology (Medical)
- Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation
- Radiation Oncology