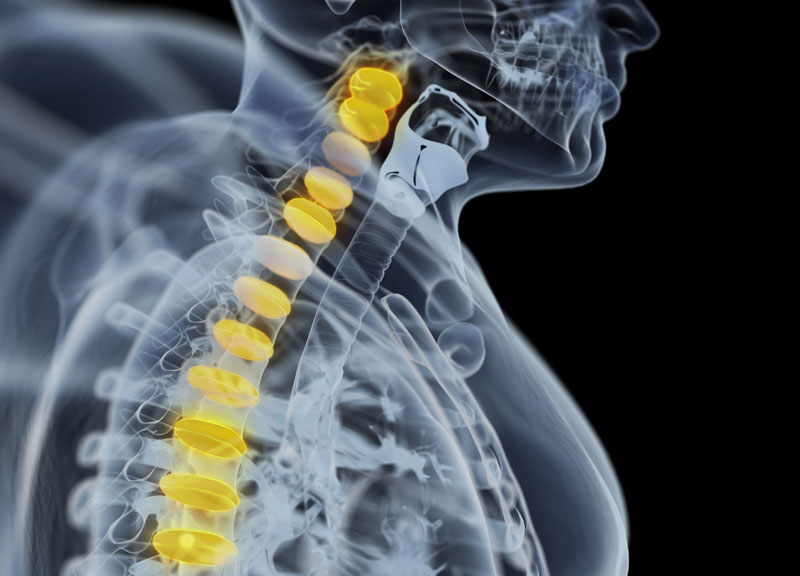
Osteoarthritis – What is it?
Also referred to as ‘degenerative joint disease’, osteoarthritis is a condition that causes degeneration or wearing down of protective cartilage that cushions the tops of bones. The condition is characterized by swelling and pain. It may even result in osteophytes (bone spurs) development.
Understanding Osteoarthritis of the Spine
Spinal osteoarthritis is a condition that causes breakdown of the joints and discs cartilage in the neck and lower back. In some cases, osteoarthritis may produce spurs that put pressure on the nerves leaving the spinal column. The patient experiences weakness and pain in the arms or legs.
Who is at Risk
Osteoarthritis is common among older individuals. Younger people may get it from one of several causes:
- Injury / trauma to a joint
- A genetic defect related to cartilage
Men younger than age 45 are more vulnerable to osteoarthritis. Women older than age 45 are more prone to developing osteoarthritis. Also, overweight / obese individuals are also highly vulnerable to the condition. Those associated with the field of sports or jobs demanding repetitive stress on certain joints.
Signs and Symptoms
Pain and Discomfort – The main symptoms of osteoarthritis of the spine include pain in the back, neck or stiffness. The condition may also result in numbness or weakness in the legs or arms. In case, it is severe enough, it may affect the spinal cord or spinal nerves. Usually, the back discomfort is relieved once the person lies down.
Problems with Daily Activities – Some individuals may experience some interference with the activities of their lives. Others may also become severely disabled.
Social / Emotional Problems – Patients with osteoarthritis may also experience social and emotional issues. For instance, an individual with osteoarthritis interfering with day to day activities and job performance may feel helpless or depressed.
Diagnosis of Osteoarthritis
Medical History – The doctor will ask for detailed medical histories of the patient.
Physical Exam – This test is very important to assess if the person suffers from any kind of pain, loss of motion, tenderness, movement issues involving the neck or lower back. The doctors will check my symptoms are suggestive, signs of nerve involvement, including reflex changes, weakness, or loss of sensation.
X-ray – It is the best way to confirm a diagnosis of spinal osteoarthritis. The test will look for any kind of bone damage, bone spurs, and cartilage or disc loss. X-rays cannot show early damage to cartilage.
Blood Tests – These tests are performed to exclude possibility of other diseases.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MR/I) – This test shows any possible damage to discs or narrowing of regions where spinal nerves exit.
Treatment Options for Osteoarthritis
Most of the treatment options for spinal osteoarthritis are aimed at relieving symptoms associated with pain and increased ability of an individual to function. Doctors aim at helping patients lead a healthy lifestyle.
Initial treatment of osteoarthritis of the spine may include a weight loss regimen if required. Maintaining a healthy weight is very important. The process may include exercise. Apart from helping with weight management, exercises help with the following:
- Enhance flexibility
- Boost attitude and mood
- Boost heart stings
- Enhance the flow of blood
- Easier undertaking of day to day tasks
Some of the exercises related to osteoarthritis treatment include:
- Walking
- Swimming
- Water aerobics
Exercise regime may be broken down into the categories mentioned below:
Range-of-motion Exercises – The exercises are helpful in enhancing flexibility of the body.
Strengthening Exercises – The exercises target muscles supporting the joints stronger. They work through resistance via using rubber bands or weights.
Aerobic Exercises – The exercises strengthens the heart and circulatory system of the body.
Rest – Short rest periods should be included in the overall treatment plan. Doctors do not recommend bed rest, bracing, splints, or traction for long periods of time.
Non-drug Treatments
- Massage therapies
- Acupuncture
- Heat or cold compresses – The patient is required to place ice or heated compresses onto the affected joint. This needs to be followed when doctors recommend it to their patients.s
- Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) – This is a process that utilizes a small device emitting electrical pulses onto the affected region.
- Nutritional supplements
Medications – The doctors may recommend pain medications to treat osteoarthritis. The most common over-the-counter products used is the acetaminophen (Tylenol).
Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) – These are recommended for patients with spinal osteoarthritis. One can get it as an over-the-counter in certain specific strengths. These drugs are known for their serious side effects such as stroke, heart attack, stomach irritation, kidney damage, etc. Some of the commonly recommended one include:
– Aspirin
– Naproxen sodium (Aleve)
– Ibuprofen (Motrin or Advil)
Topical Ointments and Creams – These are recommended to treat pain. Patients can apply it to the skin exactly in the area that hurts. However, these are usually not very effective. Some of the most common examples of topical ointments and drugs include Aspercreme and Ben-Gay.
Prescription Drugs – Doctors recommend prescription drugs to treat symptoms related to osteoarthritis of spine. Since medications do not reverse the process, these are prescribed as painkillers. Patients may also be prescribed with mild narcotics. Another option is to get injected with corticosteroids around the spinal column. These are referred to as epidural steroid injections. These do not cure or rectify the underlying problem. Patients can use it, but there is no clear indication associated with long-term benefit. Due to the possibility of serious side effects, oral steroids are not commonly used.
Surgery – Although most cases of spinal osteoarthritis can be easily treated without surgery, doctors recommend surgery sometimes. Spinal osteoarthritis is one of the major causes of spinal stenosis, also referred to as narrowing of the spinal canal. There are also cases where bladder and bowel function is impaired. The nervous system may also be damaged. Doctors recommend surgery as a treatment option when walking becomes difficult.
The information provided on this website is for informational purposes only and is not intended to take the place of consultation with your physician. Any questions that you may have regarding the diagnosis, care or treatment of a medical condition or any products described in this web site should be directed to your physician. If you are seeking specific medical advice, please contact your physician or call 911 in the case of an emergency.