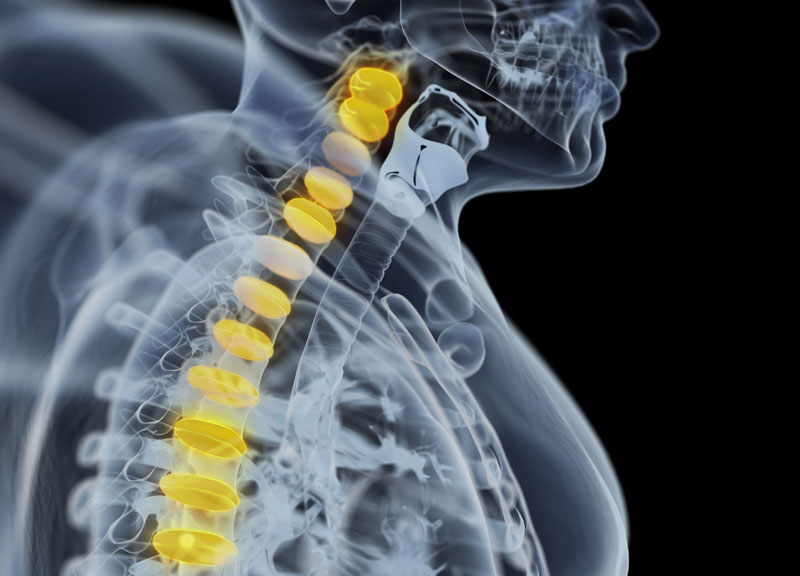
The spine comprises of 33 bones. All of these bones have a large central opening for the spinal cord. These also have additional openings known as foramen that facilitate nerves branching from the spinal cord so that these travel all the way to the legs, arms, and other parts of the body.
The nerve roots contain ample room to be able to slip through the foramen effortlessly. Unfortunately, with age and common age-related conditions such as arthritis, the foramen tend to become clogged. This invites bony spurs inside which press on the nerves. The passage through which the spinal cord runs also gets clogged. This condition is medically referred to as ‘spinal stenosis.
Signs and Symptoms
The most common symptoms of foramina stenosis may include:
- Numbness
- Burning sensations
- Weakness
- Tingling
- Pins and needles in the arms and legs
Risk Factors
As one ages, the risk of narrowing of foramen increases. The condition also increases one’s vulnerability to various other musculoskeletal conditions, such as arthritis.
Diagnosis
In order to diagnose foraminal stenosis, the doctor will assess a medical history. The doctor also conducts a physical exam wherein he will look for restrictions on movement, any loss of reflexes, pain, or other symptoms as and when the patient moves his or her spine.
Some of the other procedures are also undertaken to confirm the diagnosis. These include:
- X-rays – It helps to rule out various types of tumors, injuries or abnormalities.
- Scanning of Bone – The process helps with detecting tumors, fractures, infections and arthritis.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) – The test is very helpful in detecting damage or disease in the soft tissues such as those within the discs between ligaments or vertebrae.
- Myelogram – The process involves injecting opaque dye into the spinal column.
- Computerized Tomography (CT scan) – This will display the shape, size and adjacent structures of the spinal canal.
- MRI or CT Scan – The doctor will come to know about pressure on the spinal cord, herniated discs nerves, bone spurs, tumors etc.
Treatment Option
The traditional treatment may include:
- Pain-relieving drugs without steroids, e.g. Ibuprofen, aspirin
- Restricted activity
- Corticosteroid shots
- Exercises
- Physical therapyBraces
Surgery
In case, these treatment options are unsuccessful, a Neurosurgeon may perform a foraminotomy which is a a surgical procedure to treat foramina stenosis.