What is Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
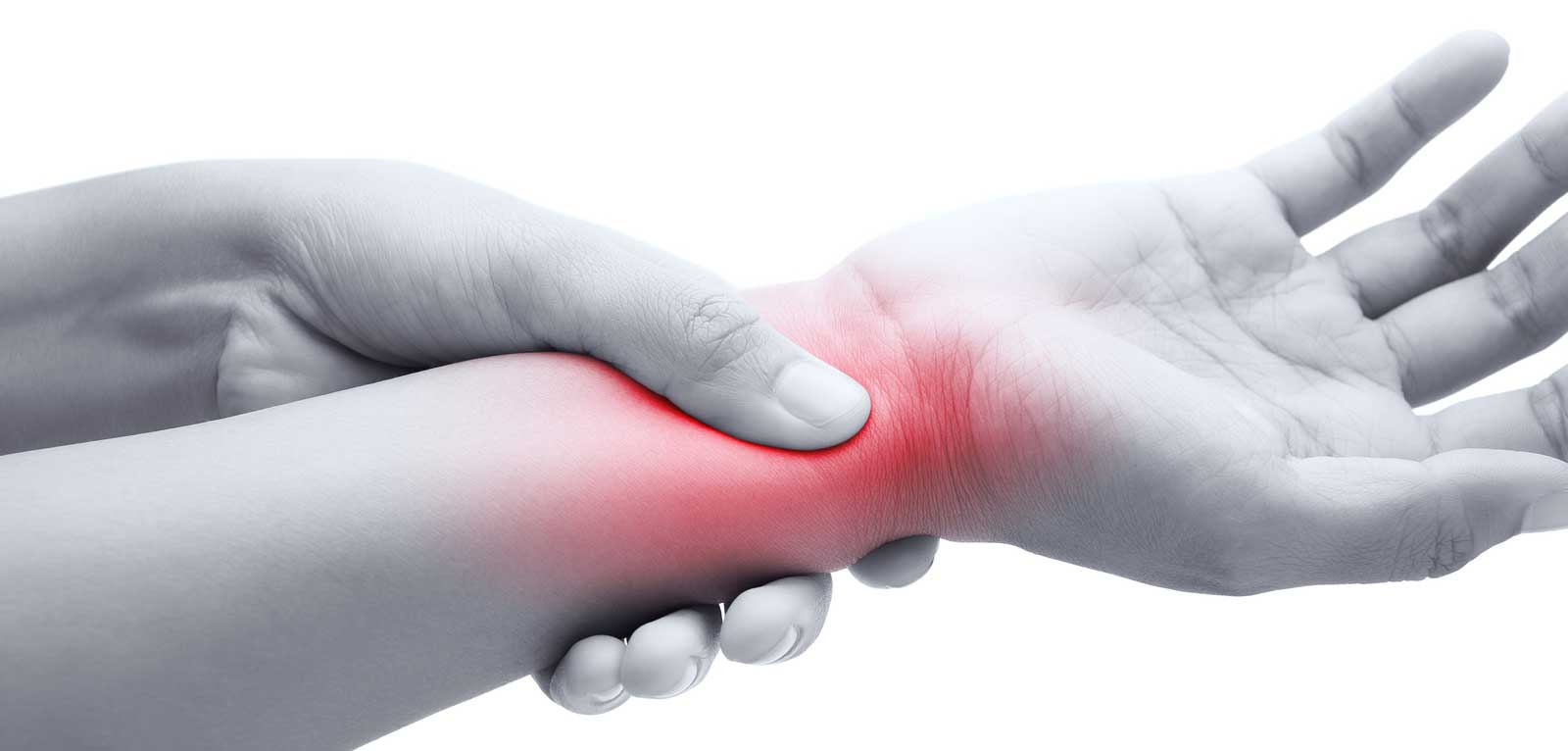
This is a hand and arm condition characterized by a feeling of tingling, numbness, and other symptoms. The major cause of carpal tunnel syndrome is a pinched nerve in the wrist. Several factors may contribute to carpal tunnel syndrome such as different hand use patterns, wrist anatomy, and some underlying health issues.
The carpal tunnel is a narrow passageway located on the wrist’s palm side. It is surrounded by bones and ligaments. The tunnel ensures protection to nine tendons of hand that help your fingers bend and a main nerve of the hand. Any compression to the nerve results in tingling, numbness, and weakness of hand weakness characterizing carpal tunnel syndrome. Luckily, carpal tunnel syndrome can be treated well with proper treatment. This relieves the tingling and numbness of the hand and restore wrist and hand function.
Signs and Symptoms
Usually carpal tunnel syndrome usually starts gradually with a feeling of numbness or tingling in the thumb, index and middle fingers. This feeling comes and goes. Sometimes, this may a reason for discomfort in the wrist and hand due to over-working them.
Other common carpal tunnel syndrome symptoms include:
Tingling or Numbness – The condition may make one feel a kind of tingling and numbness in fingers or hand. This feels more on middle, ring, index fingers or thumb (not the little finger). The sensation usually occurs when the patient holds newspaper, phone, a steering wheel, phone or wakes up from sleeping. Sometimes, the sensation may also extend to the arm. The numbness may become a constant affair as the condition progresses.
Weakness – It is possible to experience weakness in your hand. This may also lead to a tendency to drop objects due to the numbness in your hand. Sometimes weakness of the pinching muscles controlled by the median nerve.
Medical Help
In case, you observe persistent signs and symptoms that indicate presence of carpal tunnel syndrome and they start interfering with your normal day to day activities and sleep patterns, consult a medical practitioner. Leaving the condition untreated, can result in permanent nerve and muscle damage.
Causes
Usually, the main cause of carpal tunnel syndrome is compression of the median nerve. This nerve runs from the forearm through a passageway in the wrist (carpal tunnel) towards the hand. Median nerve provides sensation to palm side of fingers (not less) and thumb. It also works towards providing nerve signals to move muscles around the thumb base (motor function).
Anything that irritates, crowds, compresses the median nerve in carpal tunnel space may result in carpal tunnel syndrome. For example, wrist fracture may narrow carpal tunnel and irritate nerves. Sometimes, inflammation or swelling may result from rheumatoid arthritis. In many cases, there is no single cause for the syndrome. It may be a combination of risk factors that contributes to the development of the condition.
Understanding Risk Factors
A huge number of factors are associated with carpal tunnel syndrome. Although these factors may not cause carpal tunnel syndrome, these may increase the chances of developing or even aggravating the damage to the median. These include:
Sex – Since the carpal tunnel area is smaller in women than men, this syndrome is more common in women.
Anatomic Factors – Sometimes, dislocation of the wrist or fracture altering the space within the carpal tunnel may result in extraneous pressure especially on the median nerve. People with smaller carpal tunnels may be more likely to get carpal tunnel syndrome.
Nerve-Damaging Conditions – The risk of nerve damage increases with presence of chronic illnesses, such as diabetes.
Inflammatory Conditions – Most conditions characterized by inflammation, such as rheumatoid arthritis may affect tendons in the wrist and exert pressure on the median nerve.
Body Fluids – Changes in the balance of body fluids such as fluid retention during pregnancy or menopause tends to increase some pressure within the carpal tunnel. It irritates the median nerve. Usually, the pregnancy related carpal tunnel syndrome resolves on its own post delivery.
Other Medical Conditions – Some such as obesity, thyroid disorders, menopause, and kidney failure, can increase the chances of developing carpal tunnel syndrome.
Workplace Factors – It is quite likely that working with vibrating tools or being on an assembly line demanding prolonged or repetitive flexing of the wrist can result in harmful pressure on the median nerve.
Some studies have also revealed that computer use and carpal tunnel syndrome may be associated to a certain extent.
Tests and Diagnosis
The following tests (one or a combination of some) will be recommended by a doctor to determine the presence of carpal tunnel syndrome:
Physical Examination – The doctor conducts a physical examination by testing the feeling within fingers and muscle strength in the hand. Timing of symptoms is also noted. For instance, there are specific instances when one experience carpal tunnel syndrome symptoms such as when holding a newspaper, phone, waking up at night, gripping a steering wheel etc.
Pressure on the median nerve at the wrist, produced by bending the wrist, tapping on the nerve or simply pressing on the nerve, can bring on the symptoms in many people.
History of Symptoms – Your doctor reviews symptoms which offer clues about the cause.
X-ray – Doctors may also recommend an X-ray of the affected wrist. This helps to exclude other causes associated with wrist pain, such as a fracture or arthritis.
Electromyogram – This is used to measure tiny electrical discharges produced within the muscles. The doctor will insert an electrode (thin-needle) into specific muscles. It aims at assessing the electrical activity of muscles under different conditions such as when as they contract and are at rest. The test determines any possibility of muscle damage and help doctor rule out other conditions.
Nerve Conduction Examination – This is conducted by taping two electrodes to the skin. Thereafter, a small shock passes through the median nerve. This helps the doctor to get a clear view of electrical impulses getting slowed down in the carpal tunnel. The test is used to diagnose conditions and rule out other conditions.
A Neurologist – Doctor may recommend a detailed examination by a specialist trained in brain and nervous system conditions (neurologist). Sometimes, a brain and the nervous system surgeon (neurosurgeon) will have to examine the condition deeply.
Treatments and Drugs for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
At Premier Brain and Spine, we believe in listening to the problems faced by patients, find appropriate solutions and guaranteeing the best care. For more information on our treatment procedure for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome, request an appointment now.
It is important that Carpal tunnel syndrome gets the apt treatment as early as possible soon after the symptoms are experienced by the patient. Mild symptoms can be tackled by taking more frequent breaks and ensuring adequate rest to hands. It is also important to stay away from avoiding activities that may worsen symptoms. Application of cold packs will help ensure relief from occasional swelling.
In case, rest and application of cold packs do not work within a few weeks, doctor may recommend additional treatment options such as medications, wrist splinting, and surgery.
Splinting and other similar treatments help with mild to moderate symptoms that have been present for less than ten months.
Nonsurgical Treatment
Early diagnosis of the condition will help patients get relief by using nonsurgical methods. Some of the highly recommended and common techniques include:
Wrist Splinting – This is helpful in relieving night-time symptoms such as tingling and numbness. Here, the patient is supposed to use a splint that holds wrist still while asleep. Nocturnal splinting may be a good option if you’re pregnant and have carpal tunnel syndrome.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) – These help provide short term relief from carpal tunnel syndrome pain. Some of the commonly prescribed NSAIDs include ibuprofen such as Motrin IB, Advil, etc.
Corticosteroids – A corticosteroid may be injected by doctor into the carpal tunnel to ensure pain relief. Corticosteroids such as cortisone are helpful in reducing symptoms such as swelling, inflammation and pressure on the median nerve.
Arthritis Treatment – A special course of treatment for arthritis is recommended for carpal tunnel syndrome resulting from an inflammatory arthritis (rheumatoid arthritis).
Surgical Options
This is recommended only if symptoms get severe or persist despite trying out all of the nonsurgical treatment therapies. Surgery aims at relieving pressure on the median nerve via cutting off the ligament that presses the nerve. It may be performed with two different techniques.
Patients should have a detailed discussion of the risks and benefits of each technique with surgeon prior to surgery.
Types
Endoscopic Surgery – The surgeon uses a telescope-like device that has a tiny camera attached to it (endoscope). This helps surgeon get a clear view of carpal tunnel interiors. The surgeon can easily cut the ligament by making one or two small incisions in the wrist or hand. This surgery may result in less pain as compared to open surgery during the first few days or weeks post surgery.
Open Surgery – The surgeon makes a larger incision in the palm of hand right over the carpal tunnel. Thereafter, the ligament is cut through with an aim to free the nerve. A small incision may be made to conduct this procedure and minimize the risk of complications.
The Risks – Some of the risks associated with carpal tunnel syndrome include the incomplete release of the ligament, scarring, infections on a wound, injury to nerves, and vascular injuries.
The Healing Process
The ligament tissue grows back gradually during the healing process. This allows for more space for the nerve than before. Doctor encourages patients to use hand post surgery. In time, the patient can get back to normal use of the hand. It is important to stay away from any kind of forceful hand motions or extreme wrist positions.
Weakness / soreness is common and may take several weeks or a few months to resolve post surgery. For severe symptoms experienced by patients before surgery, the symptoms may not go away completely post surgery.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
The following steps may help patients gain temporary relief from the symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome:
- Taking frequent breaks from repetitive activities that involve the use of hands helps.
- Doctors recommend rotating of wrists and stretching of fingers and palms.
- Pain relievers like ibuprofen, such as aspirin, or naproxen help provide relief from pain.
- A wrist splint can help. This is to be worn at night. One can buy these over-the-counter at most drug stores or pharmacies. Doctors recommend splinting to be snug, not tight while wearing it.
- It is important to avoid sleeping on hands. This helps ease any numbness of pain in the wrists and hands. Most people have a difficult time overcoming this habit. However, with a little practise, one can do it.
In case, pain, weakness or numbness persists / recurs despite following the above listed remedies, consult a medical practitioner.